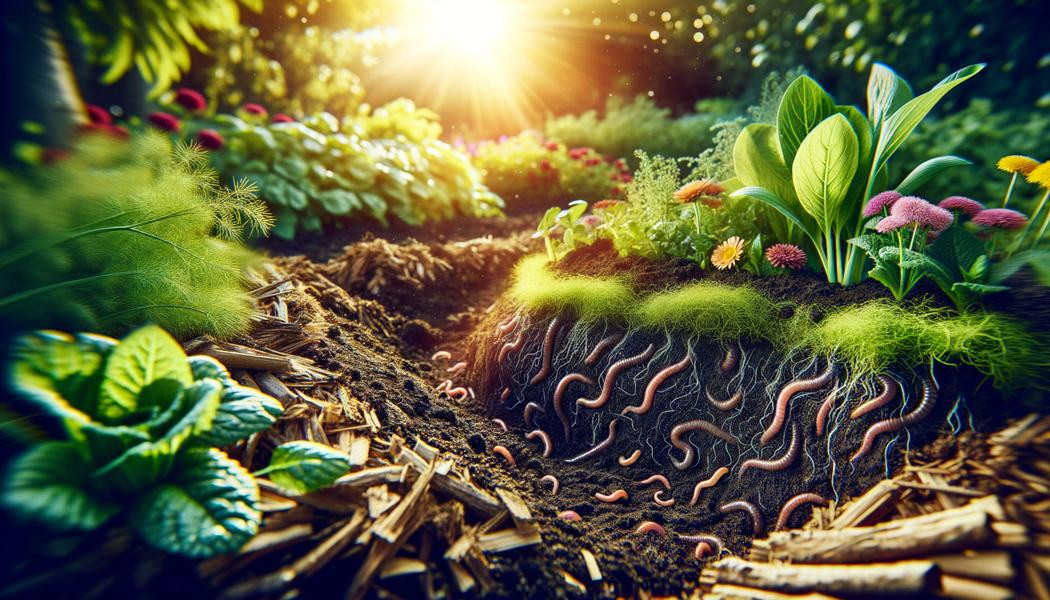


In today’s context of sustainable agriculture, optimizing soil fertility without tilling has become a crucial topic to ensure the sustainability and productivity of crops. In 2025, it is essential to explore methods that respect the ecosystem while enhancing crop yields. This article examines various aspects of optimizing soil fertility without tillage, including the advantages, effective methods, as well as the importance of biodiversity within the soil.
Need help optimizing your soil’s fertility? Quickly find a qualified provider on Helplease and enjoy a tailored service to meet all your needs. Discover professionals near you!No-till agriculture is an approach gaining more and more interest among farmers and gardeners concerned about soil health. This method preserves the soil’s natural structure, allowing various microorganisms and plant roots to develop uninterrupted. By avoiding tilling, excessive soil oxygenation is also limited, which can otherwise lead to the rapid decomposition of organic matter and thus a loss of valuable nutrients.
Furthermore, not tilling helps reduce erosion, as soil layers are held together. This is especially beneficial in regions subject to extreme weather, where water and wind can carry away the fertile top layer. By maintaining plant cover, the soil is less exposed and better able to retain moisture, which contributes to its fertility.
No-till methods also enhance rich biodiversity in the soil. Earthworms and other beneficial organisms multiply, improving soil structure, and promoting better aeration and drainage. This indirectly stimulates plant life, as roots gain better access to nutrients and water.
In conclusion, not tilling offers many advantages for soil health, leading to sustainable fertility. It fits into a holistic vision of agriculture where environmental respect and productivity go hand in hand.
Soil structure is key to ecosystem health. By avoiding tillage, compaction is prevented and a network of pores is encouraged, allowing good circulation of air and water. This preservation is also beneficial for plant roots, which can freely extend in search of nutrients.
Erosion is a major problem in many agricultural regions. Preserving the soil maintains nutrient-rich surface layers, helping keep long-term fertility. Moreover, cover crops can play a key role in soil stabilization.
Professionals, looking for more clients? Sign up on Helplease today to offer your services and develop your business. Access a wide client base in just a few clicks!Optimizing fertility without tilling the soil offers a multitude of advantages. Firstly, it preserves soil biodiversity. Beneficial organisms, such as bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi, thrive in a stable environment. These organisms play an essential role in breaking down and recycling nutrients, thus improving natural fertility without the need for added chemical fertilizers.
This approach also supports soil structure improvement. Soil that isn’t tilled retains its capillarity and allows better moisture storage. During droughts, this translates into better crop resistance. Additionally, well-structured soil limits flood risk.
Another major advantage is cost reduction. No-till optimization practices, for example, decrease the need for plowing, saving time, energy, and financial resources. Over the long term, the sustainability of this method may also reduce chemical inputs required to maintain productivity.
Finally, the method increases crop resilience to extreme climatic conditions. By maintaining plant cover and a healthy soil structure, crops are less vulnerable to diseases, pests, and environmental stresses.
By favoring a healthy ecosystem, no-till optimization ensures the preservation of soil biodiversity, which is essential for a balanced growing environment. It also helps maintain a sustainable life cycle for the soil’s various organisms.
Strengthening soil health makes crops sturdier and better able to resist diseases and pests. This natural approach promotes long-term sustainability in farming practices.
If you are seeking an expert for your specific needs, visit Helplease and discover available providers near you. Make your life easier and find the right professional!To improve soil fertility without tilling, several methods can be put into action. One of the most effective techniques is using cover crops. These plants, sown between main crops, protect the soil and increase organic matter when they decompose after harvest.
Another method is the application of compost, which brings a host of essential nutrients and promotes microbial life. Compost, rich in nutrients, not only improves soil structure but also enriches nutrients available for plants.
Mulching is also recommended. Maintaining a covered layer on the soil, mulch blocks weed germination, conserves moisture, and regulates soil temperature, encouraging an optimal growth environment.
Soil aeration is another effective method to optimize its fertility. Aeration stimulates biological activity, creating a favorable environment for plant roots and beneficial microorganisms.
Cover crops act as a natural barrier against erosion. Their growth shades the soil, conserving moisture while releasing nutrients upon decomposition.
Enriching soil with compost is extremely beneficial. It not only improves soil structure but increases its ability to retain nutrients and water, thereby boosting fertility.
The cultivation of cover crops plays a crucial role in optimizing soil fertility. These plants, often sown after the harvest of a main crop, produce bio-mass rich in nutrients. The decomposition of this biomass enriches the soil with essential elements.
Moreover, cover crops help reduce erosion by protecting the soil surface from weather. This encourages water retention, which is essential in drought-prone regions. The roots of these plants also aerate and structure the soil, allowing for better air flow and efficient drainage.
These crops help control weeds too. By covering the soil, they block unwanted plant germination, thus reducing the need for chemical herbicides. This is consistent with sustainable agricultural practices.
Finally, by encouraging botanical diversity, cover crops improve microbial and animal biodiversity in the soil. A more lively soil stores water and nutrients better, thus promoting long-term fertility.
The ability of cover crops to retain water is essential for effective resource management. They also protect against erosion, ensuring soil longevity.
By impeding the growth of unwanted plants, cover crops help reduce costs linked to herbicide use, while fostering a healthier growing environment.
Compost is an indispensable organic amendment for fostering soil fertility. For maximum effectiveness, it’s important to choose the right types of compost. Green matter compost, made from yard waste such as grass clippings, leaves or vegetable peelings, is especially rich in nitrogen and encourages vigorous crop growth.
Brown matter compost, made from straw, shredded wood, or dry leaves, provides essential carbon elements for soil balance. Combined with green matter compost, it forms a balanced mix, encouraging proper decomposition and a diverse nutritional supply.
Manure compost is also highly valued. Rich in nutrients, it improves soil structure and supports bacterial life, which is crucial for nutrient recycling. It’s important, though, to compost it thoroughly to avoid disease vectors.
Lastly, mushroom or mycelium compost, though still relatively rare, fosters increased soil biodiversity, thereby strengthening its natural ability to maintain fertility.
Rich in nitrogen, green matter compost jump-starts crop growth and rapidly enriches the soil.
Brown matter compost fosters balance by providing important carbon elements for soil life.
Mulching is an effective method to maintain soil fertility. By applying a layer of organic material, such as wood chips, dead leaves, or hay, a protective cover is created on the soil surface. This shield prevents rapid soil dehydration by conserving moisture and regulating temperature.
Mulching also limits the growth of weeds, reducing competition for nutrients and water between crops and unwanted plants. This allows cultivated plants to grow more efficiently.
As mulch decomposes, it enriches the soil by supplying essential nutrients. This fosters a living and dynamic soil, beneficial to crop growth.
Finally, mulching helps fight erosion, especially during heavy rain. By reducing the impact of water on the soil, it protects the fertile surface and preserves soil structure.
By maintaining high moisture levels, mulching encourages optimal root growth and reduces drought stress on plants.
By limiting weed germination, mulching saves time and resources for weeding.
Soil aeration is a practice that boosts fertility optimization. By allowing air to circulate through the soil, it stimulates biological activity. Microorganisms and earthworms flourish, contributing to the breakdown of organic matter and the recycling of nutrients.
Aeration also helps prevent soil compaction, a common problem that restricts the movement of water and nutrients, making it hard for roots to access these essentials. This ensures better root anchorage and growth.
Finally, good soil aeration optimizes drainage, reducing the risk of saturation and fungal diseases that can harm crops.
In summary, soil aeration leads to a healthy and productive environment, helping plants grow and access the nutrients they need.
Better aeration supports microbial and animal life in the soil, boosting overall soil health and fertility.
Avoiding compaction is vital to guarantee roots optimal access to water and nutrients, supporting healthy plant growth.
Earthworms play a vital role in optimizing soil fertility. They help create good soil structure, especially through their ability to dig channels in the soil, improving air and water circulation. This allows plant roots to develop better.
Moreover, worm castings, also known as vermicompost, are amendments rich in nutrients that greatly enhance soil fertility. These nutrients are sometimes more easily absorbed than those found in regular compost.
Earthworms feed on decomposing organic matter, enriching the soil in nutrients while supporting microbial activity. By integrating earthworms, soil life is thus stimulated, which is essential for maintaining fertility.
To encourage the presence of earthworms, it is important to use farming practices that preserve their habitat, such as reducing soil tillage and using organic matter for mulching and composting.
Galleries made by earthworms allow not only better aeration but also water retention, creating an optimal living space for plants.
Vermicompost, resulting from worm castings, is a rich, bioavailable amendment that greatly aids in improving fertility.
To improve soil structure and fertility, certain plants are especially effective. Legumes, such as clover and peas, play an essential role by fixing nitrogen in the soil, a key nutrient for crop growth. These plants can increase soil fertility while also improving structural properties.
Deep-rooted plants, like sunflowers or radishes, help aerate and loosen the soil. Their root systems also extract nutrients from deep down, bringing them to the surface when the plant decomposes.
Cover crops, such as rye and oats, help maintain continuous soil cover, thus reducing the risk of erosion. They also encourage biodiversity, which benefits fertility.
Finally, herbal plants such as basil or thyme, offer benefits as companion plants by repelling certain pests and fostering favorable conditions for neighboring crops.
Legumes enrich the soil with nitrogen, which is vital for plant growth.
Certain plants help break up compacted soil and enrich the surface with nutrients thanks to their root systems.
Nutrient-poor soil may show several obvious signs. The first indicator is stunted plant growth, marked by yellowing or discolored leaves, often showing a lack of nitrogen or other essential nutrients. In addition, poor flowering and weak fruiting may also indicate nutrient deficiencies.
Persistent weeds can also indicate soil imbalance, with a dominance of less nutritious species. The soil texture may change, showing compaction or excessive dryness, which restricts access to water and air. If soil acidity is high, pH tests may reveal unfavorable conditions for healthy crops.
To remedy these problems, adding compost or organic matter can restore balance. Crop rotation is also an effective method to prevent nutrient depletion, as is the introduction of mineral amendments when needed.
In conclusion, regularly monitoring soil health and making the right adjustments can quickly restore its fertility, optimizing crop yields.
Seeing plants fail to develop properly is a clear sign of neglected soil, often caused by a lack of nutrients.
Weeds taking over growing space can indicate a nutrient deficiency or imbalance in the soil.
Crop rotation is an age-old practice that plays a fundamental role in sustaining soil fertility. By alternating crop types planted on the same land, nutrient depletion is avoided since each species has specific needs.
This practice also prevents the buildup of pathogens and pests that could establish themselves if only one crop were grown year after year. Including various plants supports biodiversity, which strengthens farming systems’ overall resilience.
Additionally, crop rotation helps improve soil structure by reducing compaction. The different roots encourage aeration and water infiltration, thus increasing the soil’s ability to retain nutrients.
Finally, rotation enhances crop yields, as it helps create a healthier, more balanced growing environment. This maximizes production while reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
By varying crops, pest populations are restricted, protecting both soil and harvests.
Rotation supports optimal aeration, fostering a healthy environment for roots and microorganisms.
Assessing soil fertility is essential before any optimization. A soil test analyzes nutrient content, pH, and texture, providing a precise overview of what needs to be strengthened. Many laboratories offer affordable soil testing services that recommend necessary amendments.
Observing plant growth over a season is also important. Signs of nutritional deficiencies, such as leaf yellowing or poor development, indicate soil needing special attention.
It’s also useful to monitor soil biodiversity. The presence of worms, microorganisms, and other creatures often signals healthy, fertile soil. Finally, evaluating the soil’s ability to retain moisture is essential; soil that dries out quickly may require amendments to improve its structure.
In summary, establishing a thorough diagnosis of soil health will define the best optimization techniques to implement, ensuring healthy and productive crops.
Conducting soil tests provides precise data about soil composition and characteristics, making it easier to make informed decisions about which practices to use.
Monitoring crop performance over the seasons is crucial to identify nutrient needs and adjust practices accordingly.
Whether you need quick help or want to offer your services, Helplease is your solution! Download the app to access qualified experts or find clients in one click, and simplify your daily life! Available on iOS and Android!