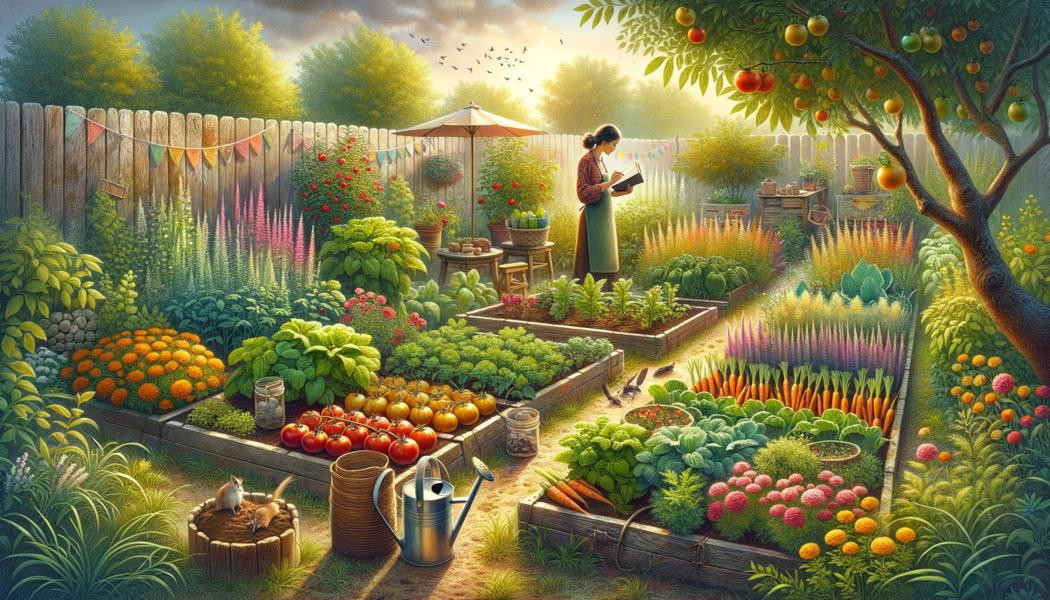


Growing a self-sufficient vegetable garden is an exciting adventure that not only allows you to produce your own vegetables but also to do so sustainably and with respect for the environment. This article will guide you through the essential steps to start a self-sufficient vegetable garden, with practical advice tailored for beginners. Through twelve detailed sections, we will explore the basics, crop selections, resource management, and much more to help you succeed in your new undertaking.
Do you need help cultivating a self-sufficient vegetable garden? Quickly find a qualified provider on Helplease and benefit from a tailor-made service to meet all your needs. Discover professionals near you!A self-sufficient vegetable garden is a cultivation system aimed at producing vegetables independently, relying on available natural resources and minimizing the use of external inputs, such as chemical fertilizers or pesticides. Autonomous gardening is sustainable and environmentally friendly, seeking to create a balance that encourages biodiversity, healthy soil, and a favorable microclimate. This type of garden is important as it addresses today’s ecological challenges, including combating pollution, reducing carbon footprint, and promoting local food sources.
Additionally, a self-sufficient garden allows you to enjoy fresh, healthy produce while reducing the costs associated with purchasing vegetables at the supermarket. Growing your own food also gives you the opportunity to choose varieties that suit your tastes and to follow an ecological approach by respecting seasons and natural cycles. It strengthens the bond between people and nature, while offering a gratifying and relaxing activity. Moreover, by growing your own vegetables, you promote food sovereignty, which has become a major concern in modern societies.
Thus, a self-sufficient vegetable garden becomes a place of learning, experimentation, and sharing. It is the ideal space to discover the subtleties of plant cultivation, but also to understand the interrelationships that characterize ecosystems. Gardeners of a self-sufficient garden learn to observe and adapt to their plants’ needs while incorporating practices that respect natural resources. Beyond simply producing vegetables, cultivating a self-sufficient garden is a true act of environmental responsibility.
In summary, a self-sufficient vegetable garden not only enables you to feed yourself more healthily and mindfully, but also constitutes a step towards a sustainable life, in harmony with your environment. For all these advantages, it is essential for a beginner to understand what is involved in creating and maintaining a self-sufficient vegetable garden.
Growing your own garden offers numerous benefits. First, it allows you to produce pesticide-free, fresh food leading to better health. Then, a garden reduces the costs related to buying fruits and vegetables, and supporting a local diet is essential for the environment. Moreover, it is a beneficial physical and mental activity, contributing to stress reduction and overall well-being.
A self-sufficient vegetable garden helps preserve biodiversity by fostering the coexistence of a wide range of plants. It also contributes to soil health by encouraging living organisms that maintain a balanced ecosystem. Additionally, by limiting trips to the grocery store, a self-sufficient garden reduces its owner’s carbon footprint.
To start a self-sufficient vegetable garden, it is necessary to understand a few fundamental principles. Firstly, it is vital to respect the natural cycle of the seasons, which implies researching which vegetables are suitable for each part of the year. The ideas of crop rotation and diversification are also crucial to maintain soil health and prevent diseases from appearing. This means moving certain plant families around and alternating crops between these different families.
It is also important to observe the behavior of plants and insects in your garden to adapt your growing methods. Observation is a key element in understanding the ecosystem you are creating. Using techniques such as lasagna gardening or permaculture mounds can facilitate plant growth while conserving water.
Planning and design are preliminary steps that every gardener must consider carefully. A well-designed garden makes plant access easier, optimizes sun exposure, and allows air to circulate well, thereby limiting diseases. Also, accounting for the space needed by each plant when designing your garden helps avoid competition among crops.
Lastly, take care to nourish and enrich the soil by incorporating homemade compost and using organic fertilizers. The nutritional balance of the soil is essential for plant growth. Getting to know your soil’s qualities and needed amendments will allow you to create a fertile environment that’s ideal for developing your self-sufficient vegetable garden.
Good planning is essential for a successful self-sufficient vegetable garden. This includes choosing the location, selecting the plants, as well as designing the layout. A thoughtful design helps optimize space and improve accessibility. Consider using beds, mounds, or trellises to structure your garden and make productive use of every square meter.
Observation is a valuable tool in gardening. It allows you to spot early signs of stress in your plants, identify pests, and understand how your garden is evolving. Record your observations to better adjust your actions and improve your growing practices. Quickly adapting your methods based on what you observe in your garden is key to achieving an autonomous system.
Choosing the right location for your garden is crucial to ensure the success of your crops. It is advised to select a spot with at least six hours of direct sunlight per day. Vegetables, in particular, need light in order to be productive. Avoid shaded areas caused by trees, buildings, or other obstacles that could inhibit their growth.
Furthermore, good drainage is essential. Heavy or water-retaining soils can cause root rot and other serious problems. Choose a plot that allows excess water to drain away. If the land is too damp, consider creating raised beds to elevate your plants and avoid waterlogging.
Access to water is also a fundamental criterion. Ensure your garden is easily accessible for watering, and set up a simple irrigation system, such as a watering can or hose. The closer your garden is to a water source, the less likely you’ll forget to water it.
Also, pay attention to prevailing winds. Strong winds can damage your plants, especially young seedlings. If your area is exposed to strong winds, design your garden with protective structures, like hedges or windbreaks.
Sufficient sunlight is the key to photosynthesis, helping plants develop and bear fruit. Examine the area at different times of day to ensure proper light exposure. Also consider the height of the plants you will grow, since some may shade others. Avoid planting larger varieties that could hinder the growth of nearby plants.
Accessibility is another factor not to ignore when choosing your garden’s location. Ensure the space is wide enough for you to move around easily, with convenient access for maintenance. Think about how you will water, weed, and harvest vegetables, since a garden that is difficult to access can discourage regular upkeep.
Self-sufficient vegetable gardening draws upon several ecological practices that create a healthy environment for plants. One of the most popular methods is permaculture, which involves designing growing systems inspired by natural ecosystems. This includes planting species that help each other by offering mutual protection against diseases and pests.
Lasagna gardening is another effective method, creating layers of organic material to feed the soil as it decomposes. This technique enriches the soil without the need for chemical fertilizers while improving its structure. Additionally, mulching—covering the ground with several centimeters of organic matter—helps to retain moisture and limit weed growth.
Mound gardening is also an excellent method, enabling better water management and encouraging early soil warming. Alternatively, the raised bed garden technique ensures good drainage and can be adapted to smaller spaces. These techniques help optimize space usage while increasing crop productivity.
Finally, applying best practices in crop rotation helps maintain soil fertility. By avoiding planting the same species in the same place year after year, the risks of diseases and pests are reduced, while the soil regenerates and retains its nutrients.
Gardening with relief, such as mound or lasagna gardening, promotes better soil aeration and allows for greater plant diversity. These techniques help efficiently distribute water and nutrients. By also integrating ground-cover plants, you decrease empty spaces where weeds could settle, while protecting the soil.
Using natural resources such as green waste, dead leaves, and manure lets you create a sustainable, self-sufficient ecosystem. By integrating these elements into composting, you’re repurposing waste while improving your soil’s fertility, which boosts your self-sufficient garden’s viability.
The choice of plants is a determining factor in the success of your self-sufficient garden. Vegetables that thrive in natural ecosystems are often best adapted. Stalk vegetables, such as leeks or onions, are generally easier to grow than fruiting vegetables like tomatoes, which need specific care.
Furthermore, short-cycle vegetables like radishes or lettuces allow you to achieve quick harvests and enjoy production while improving soil structure. Also consider adding aromatic plants, such as mint or basil, which not only add flavor to your dishes but also attract pollinators.
Another important aspect is the potential for growing companion plants. Certain species, such as basil and tomatoes, help each other grow better when cultivated together. Study the plants carefully to create beneficial associations, as this helps deter some pests and improves each species’ yield.
Lastly, choose local or heirloom varieties adapted to your region’s climate. These varieties are often more resistant to diseases and better acclimated to local conditions, allowing your self-sufficient garden to thrive in the long run.
Growing seasonal vegetables leads to better production and a garden that matches natural cycles. Prioritize vegetable varieties adapted to each season, such as winter crops like cabbages and carrots, and summer vegetables like zucchini and melons. Respecting these natural rhythms will grant you larger and tastier harvests.
The association of certain plants can significantly enhance your garden’s productivity. For example, planting flowers like nasturtium or calendula will attract pollinators and naturally repel certain pests. Moreover, cultivating nitrogen-fixing plants such as beans will promote your soil’s fertility.
Composing beneficial plant associations means taking into account the affinities between species. Companion plants boost productivity by deterring pests or promoting plant growth. For instance, tomatoes and basil are often grown together for their complementarity.
Other associations act as barriers against pests. For example, blueberries and peas help mutually protect crops. Furthermore, some plants produce essential oils that can repel insects. By judiciously combining these, you increase your garden’s resilience.
Be sure to respect nutritional needs and light requirements among different species. Some plants, such as corn, provide a natural support for climbing crops like beans or squash, enabling optimal use of space and enhancing each plant’s productivity.
Document your association results to improve future gardening practices. Some combinations may produce unexpected results, so it is vital to adapt your experiments and keep learning.
Companion planting is a principle of sustainable agriculture. Each species can balance the ecosystem in your garden. Take notes on every association to see which combinations work best. This allows you to adjust your methods and deepen your ecosystem knowledge.
Learning to recognize signs of plant stress is crucial for maintaining healthy crops. By observing leaf color, flower size, and fruit development, you can anticipate and correct potential problems. Healthy plants are also more resistant to pests and diseases.
Insects and animals play a crucial role in the ecosystem of a self-sufficient garden, participating in pollination, regulating pest populations, and aerating the soil. Bees, for example, are essential for pollinating many crops. Without them, more than 80% of crops would bear fruit poorly or not at all.
Additionally, predatory insects such as ladybugs, hoverflies, and parasitoid insects prey on pests like aphids, ensuring a natural balance. Avoiding pesticide use helps preserve these natural allies, who protect your crops efficiently.
Animals, such as earthworms, also play a key part in maintaining your garden. They aerate the soil, facilitate water infiltration, and transform organic matter into humus. Your garden’s proper functioning relies on the harmonious interaction of these living organisms, each of which has its role.
Observing insects and animals in your garden can also provide clues about its overall health. The presence of a large variety of insects is generally a sign of biodiversity, while absence or imbalance may indicate something is wrong. It is an excellent indicator of your garden’s state.
Pollinators are vital for the development of your crops. To encourage their presence, plant flower species that attract them. Floral diversity has a direct positive impact on pollination, so diversify your garden with flowers like asters, lavender, and marigolds.
Encouraging the presence of natural pest predators is an effective way to maintain garden health. Installing birdhouses or insect hotels will attract predators such as insect-eating birds and bats, both of which play a key role in pest control.
Water management is an essential aspect of maintaining a self-sufficient garden. Efficient management conserves water while ensuring your plants are properly hydrated. Several techniques can be used, such as mulching, which helps retain soil moisture and reduces watering needs.
Installing a rainwater harvesting system can also be very beneficial. It gives you water with no extra cost and lessens reliance on public water supply. Make sure to design drainage properly to prevent contamination and maximize collection.
Additionally, it is recommended to water in the evening or early morning, when the sun is less intense. This prevents water from evaporating too quickly, ensuring your plants are adequately hydrated. Proper watering also reduces the risk of diseases, as dry leaves are less susceptible to fungi.
Lastly, using gardening tools such as drip irrigation systems makes it easier to meet plants’ water needs. These systems target plant roots directly with measured flows, maximizing irrigating efficiency and minimizing waste.
Conserving water should become a priority when growing a self-sufficient garden. Mulching helps retain soil moisture, while managed irrigation systems optimize water use. Pay attention to watering frequency, and adapt to your climate conditions and plant needs.
Learn to assess soil moisture. You can run a simple test by pushing your finger into the soil—if it feels moist up to the first knuckle, there’s no need to water yet. This will help you save water and provide optimal irrigation for your crops.
Adopting natural pest management strategies is fundamental in a self-sufficient garden. Using tips such as crop rotation and planting resistant varieties can prevent infestations. By diversifying your crops, you disrupt pests’ reproductive cycles and limit their impact.
Integrating repellent plants can also be very effective. For example, the strong scents of herbs such as thyme, rosemary, and mint can discourage many pests. Use them as borders or companion plants to protect your crops.
Creating physical barriers—like nets or cloches—can reduce pest access to your plants. Especially for fragile crops or seedlings, these protections can be an effective solution to prevent damage.
Finally, natural predatory insects are an efficient way to control pests. Encourage their presence by providing a habitat for ladybugs, spiders, and other beneficial insects that regulate pest populations in your garden.
Incorporating repellent plants is a simple yet often underutilized technique. Plants like mint, marigold, and nasturtium have properties that can reduce the presence of many pests. Be sure to integrate these plants throughout your garden to maximize their benefits.
Attracting predatory insects such as ladybugs and hoverflies will help control pest populations. Creating an environment attractive to these predators—by planting nectar-rich flowers—will increase your chances of effective pest control in your garden.
Successfully harvesting your vegetables at the right time is crucial for ensuring quality and flavor. Each vegetable has an optimal time for harvesting according to its growth cycle. Knowing the signs of ripeness is therefore essential. For example, tomatoes should be picked when their color is fully developed and they feel slightly firm to the touch.
Generally, leafy vegetables such as lettuce can be picked when their leaves are large enough to eat. This harvesting method allows for continuous production, as the remaining leaves will keep growing. For roots like carrots or beets, wait until the soil is well loosened so that you can easily lift them out without damage.
Harvesting early in the morning or late afternoon is ideal when temperatures are cooler. This preserves the freshness of your vegetables and reduces plant stress. Place your harvest in baskets or breathable containers to maintain quality until you are ready to prepare them.
A good harvest also means avoiding damaging plants; make sure to use harvesting tools such as scissors or secateurs for clean cuts, causing no harm to the plants. Finally, be sure to identify specific varieties that must be harvested in special ways, as each vegetable has its own requirements.
Knowing how to recognize signs of maturity is essential. Vegetables like peppers should be ripe to be eaten, while squashes are harvested when they are firm and shiny. Learning to identify these clues is an invaluable skill for every gardener.
Make sure to store your harvests properly to prolong shelf life. Some vegetables can be stored in a cool, dark place, while others should be placed in the refrigerator. Be mindful of the specific storage needs of each vegetable to make the most of your harvests.
When starting a vegetable garden, there are several common mistakes that beginners often make. One of the main errors is choosing plants unsuited to the climate and season. Above all, identify your region’s climate to select compatible varieties. Don’t be tempted by vegetables that require special climates unless you are ready to create the necessary conditions for them.
Another frequent mistake is neglecting the soil. Poorly prepared soil can lead to serious growth problems. Test your soil to learn its pH and composition, and enrich it with organic amendments if necessary. Don’t underestimate the importance of fertile, well-aerated soil for your garden’s success.
Avoiding overcrowding is also crucial. Planting too many vegetables in a small space can lead to competition, limiting plant growth. Respect planting distances so that each plant can fully develop.
Finally, a commonly forgotten mistake is failing to research each plant’s specific needs. Every crop has its unique requirements, ready to be learned. Be patient and study the best practices for each one to optimize your harvest.
Attempting hard-to-grow crops can be discouraging. Don’t hesitate to ask other gardeners for advice or consult books and online resources to know which vegetables are best for your area. Making the right choices will boost your gardening enjoyment and increase your chances of success.
A vegetable garden requires commitment to maintenance. If you leave your plants unattended for too long, it can lead to their decline. Set up a maintenance calendar for weeding, watering, and fertilizing your crops so you stay organized and avoid feeling overwhelmed.
Composting is an essential technique for enriching your self-sufficient garden with organic matter. By turning your kitchen and garden waste into compost, you create a natural amendment rich in nutrients that promotes soil health. To get started, gather a balanced mix of green materials (vegetable peelings, grass clippings) and browns (dead leaves, cardboard), to ensure a good carbon/nitrogen ratio.
Ensure your compost decomposes properly by turning it regularly. Moisture also plays a key role; keep your compost moist but not soggy. In return, your plants will reward you with healthy, robust growth.
Besides being an excellent amendment, composting is a sustainable solution to reduce household waste. You minimize your ecological footprint while creating a virtuous cycle that benefits your garden and respects the environment.
In conclusion, composting is an integral part of autonomous gardening. By making it a regular practice, you maximize your garden’s productivity while supporting a sustainable and responsible lifestyle.
To create your compost, choose a suitable, shaded, and easily accessible location. A composter or simply a compost heap will work. Pay attention to the layers you add for good aeration and the ideal balance between green and brown materials.
When your compost is ready, it becomes a valuable amendment to incorporate into your garden soil. Add it when preparing the soil in spring or spread it around your plants throughout the year for continuous nutrient enrichment. This will foster fertile soil that supports the various crops in your self-sufficient garden.
In short, cultivating a self-sufficient vegetable garden is a rewarding journey that requires preparation, passion, and respect for nature. By following these practical beginner’s tips, you can set up a garden that will provide you with fresh, healthy vegetables while supporting the environment. From understanding the basics to efficient water management and beneficial plant associations, every aspect of autonomous gardening contributes to a flourishing garden’s success. By integrating composting, you add an extra dimension to your ecological and sustainable approach. Take the time to learn, observe, and adjust your practices to fully enjoy your garden while supporting an environmentally friendly lifestyle.
Whether you need quick help or want to offer your services, Helplease is your solution! Download the app to access qualified experts or find clients in just one click, and simplify your daily life! Available on iOS and Android!